 数据提取之正则
数据提取之正则
# 数据提取之正则
# 学习目标
- 掌握 正则表达式的常见语法
- 掌握 re模块的常见用法
- 掌握 原始字符串
r的用法
# 1 什么是正则表达式
用事先定义好的一些特定字符、及这些特定字符的组合,组成一个规则字符串,这个规则字符串用来表达对字符串的一种过滤逻辑。
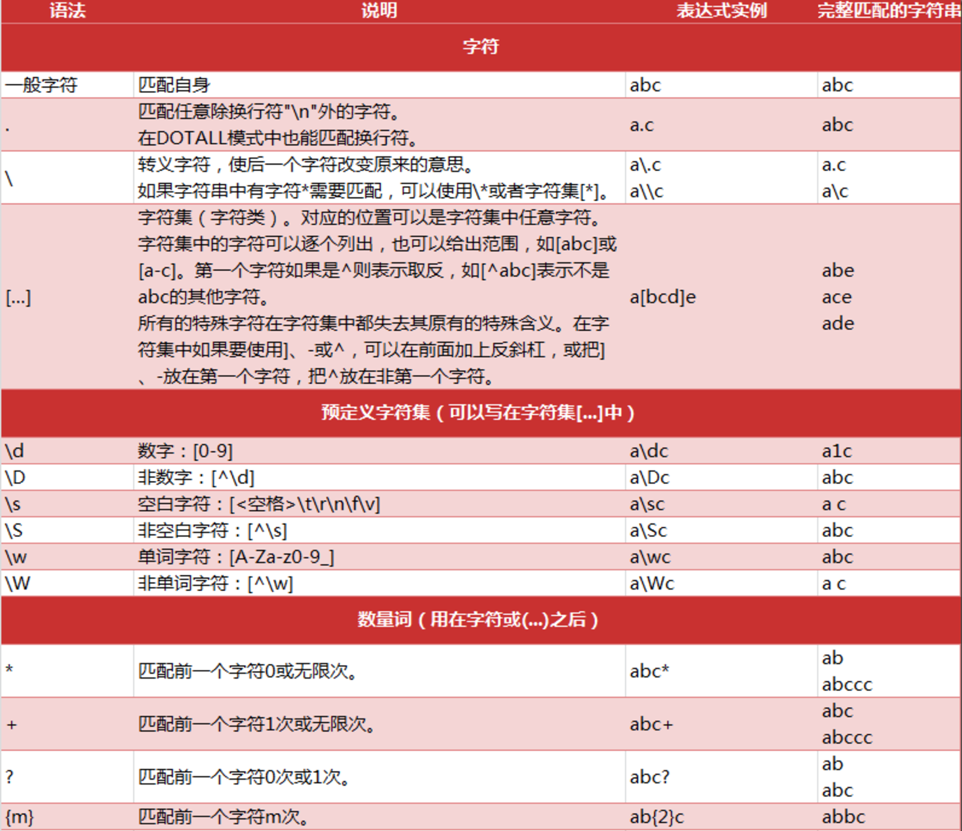
# 2 正则表达式的常见语法
知识点
- 正则中的字符
- 正则中的预定义字符集
- 正则中的数量词
练习: 下面的输出是什么?
import re
string_a = '<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">\n\t\t<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">\n\t\t<meta content="always" name="referrer">\n <meta name="theme-color" content="#2932e1">'
ret = re.findall("<.*>",string_a)
print(ret)
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
输出内容如下:
['<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1">', ...]
# 3 re模块的常见方法
re.match(从头找一个)
re.search(找一个)
re.findall(找所有)
- 返回一个列表,没有就是空列表
re.findall("\d","chuan1zhi2") >> ["1","2"]
re.sub(替换)
re.sub("\d","_","chuan1zhi2") >> ["chuan_zhi_"]
re.compile(编译,提升匹配速度)
- 返回一个模型P,具有和re一样的方法,但是传递的参数不同
- 匹配模式需要传到compile中
p = re.compile("\d",re.S)
p.findall("chuan1zhi2")
1
2
2
# 4 python中原始字符串r的用法
原始字符串定义(raw string):所有的字符串都是直接按照字面的意思来使用,没有转义特殊或不能打印的字符,原始字符串往往针对特殊字符而言。例如"\n"的原始字符串就是"\\n"
- 原始字符串的长度
In [19]: len("\n")
Out[19]: 1
In [20]: len(r"\n")
Out[20]: 2
In [21]: r"\n"[0]
Out[21]: '\\'
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 正则中原始字符串的使用
In [13]: r"a\nb" == "a\\nb"
Out[13]: True
In [14]: re.findall("a\nb","a\nb")
Out[14]: ['a\nb']
In [15]: re.findall(r"a\nb","a\nb")
Out[15]: ['a\nb']
In [16]: re.findall("a\\nb","a\nb")
Out[16]: ['a\nb']
In [17]: re.findall("a\\nb","a\\nb")
Out[17]: []
In [18]: re.findall(r"a\\nb","a\\nb")
Out[18]: ['a\\nb']
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# 上面的现象说明什么?
- 正则中使用原始字符串
r能够忽略转义符号带来的影响,加上原始字符串r之后,待匹配的字符串中有多少个\,正则中就添加多少个\即可
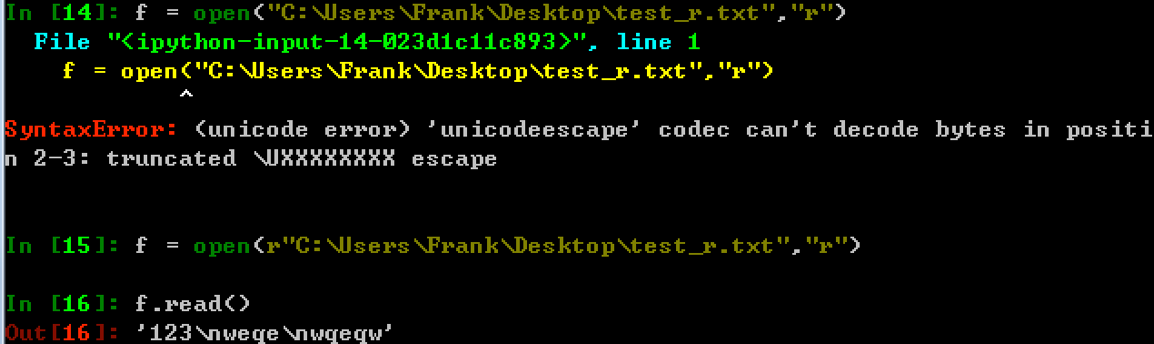
windows中原始字符串r的使用
# 5 匹配中文
在某些情况下,我们想匹配文本中的汉字,有一点需要注意的是,中文的 unicode 编码范围 主要在 [u4e00-u9fa5],这里说主要是因为这个范围并不完整,比如没有包括全角(中文)标点,不过,在大部分情况下,应该是够用的。
假设现在想把字符串 title = u'你好,hello,世界' 中的中文提取出来,可以这么做:
import re
title = u'你好,hello,世界'
pattern = re.compile(ur'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')
result = pattern.findall(title)
print result
# 注意点: 中文匹配 需要设置unicode字符才可以匹配
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 6 练习
- 如何非贪婪的去匹配内容?
import re
s = '123xxxxxx456'
result_1 = re.findall('\d+', s)
result_2 = re.findall('\d+?', s)
print(result_1)
print(result_2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 7 动手
通过正则匹配果壳问答上面的精彩回答的地址和标题https://www.guokr.com/ask/highlight/?page=1 (opens new window)
思路:
1. 寻找url地址的规律

2. 寻找数据的位置

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 小结
- re模块的常见方法:match,search,find,findall)
- 原始字符串
r的用法(保持原先字符串中所有的字符)
编辑 (opens new window)
