 Express源码解析
Express源码解析
# # Express源码解析
nodejs使得可以用javascirpt语言编写后台应用,但使用原生nodejs开发web应用非常复杂。Express是目前最流行的基于Node.js的Web开发框架,可以快速地搭建一个完整功能的网站。以下结合开发文档 (opens new window) (opens new window)和express源码 (opens new window) (opens new window),整理出常用的一些API以及路由机制源码,使得读者理解更加通透。
# # Express
- static class
Router()创建一个router对象static()设置静态资源根目录,基于serve-static (opens new window) (opens new window)模块
- instance
- 路由相关
app.use(path, callback)主要用来添加非路由中间件,底层调用router.use()。- 匹配Path的方式:
- 路径: /abcd
- 路径模式: /abc?d
- 正则表达式: //abc|/xyz/
- 数组合集: ['/abcd', '/abc?e', //abc|/xyz/]
- 匹配Path的方式:
app.all/METHOD(path, callback [, callback ...])注册一个http请求路由app.route(path)获得route实例
- 实例方法
app.get(name)获取app上定义属性app.set(name, value)绑定或设置属性到app上app.listen()跟Node的http.Server.listen()一致
- 路由相关
大部分情况app.use()和app.all()使用相似,最大不一样是中间件执行顺序。app.use()针对主进程,放前面跟放最后不一样;但app.all针对应用的路由,放的位置与中间件执行无关。stackoverflow (opens new window) (opens new window)
var express = require('express')
var logger = require('morgan')
// 中间件
app.use(logger()) // 每次都记录日志
app.use(express.static(__dirname+'/public'))
// 路由
app.get('/api', (req, res) => res.send('api router'))
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('success'))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# # Router
跟express路由API相似:
router.use(path, callback)router.all/METHOD(path, [callback])router.route()
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
// method方式路由
app.get('/api', (req, res) => res.send('api router'))
app.get('/api/:id', (req, res) => {
res.send('api detail')
})
// method多回调路由
var cb0 = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('CB0');
next();
}
var cb1 = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('CB1');
next();
}
var cb2 = function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from C!');
}
app.get('/example/c', [cb0, cb1, cb2]);
// app.route方式路由
app.route('/example/d')
.get(function(req, res) {
res.send('Get a random book');
})
.post(function(req, res) {
res.send('Add a book');
})
.put(function(req, res) {
res.send('Update the book');
});
// 子路由方式
var router = express.Router();
router.get('/user/:id', function (req, res) {
res.send('OK');
});
router.post('/user/:id', function (req, res) {
res.send('Post OK');
});
app.use('api', router);
app.listen(3000);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# # Request
Express Request扩展了node http.IncomingMessage类,主要是增强了一些获取请求参数的便捷API。源代码在这 (opens new window) (opens new window)
req.headers``extend http返回header object对象req.url``extend http返回除域名外所有字符串req.method``extend http返回请求类型GET、POST等req.get(name)/req.header(name)底层调用node http 模块的req.headersreq.params返回参数对象,对应的属性名由定义路由时确定。比如app.get('/user/:id')路由时,可以通过req。params.id取得参数req.query返回查询参数object对象。等同于qs.parse(url.parse(req.url,true).query)。req.path返回字符串。等同于url.parse(req.url).pathname。pathname跟req.url比,不带query后缀req.bodypost请求获取到数据。需要使用body-parser (opens new window) (opens new window)中间件req.cookies拿到cookies值。需要使用cookie-parser (opens new window) (opens new window)中间件
// http://localhost:3000/api/1?type=123
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.query) // { type: '123' }
console.log(req.path) // /api/1
console.log(req.params) // can got req.params.id
console.log(req.body) // usually in post method
console.log(req.cookies) // need cookie-parser middleware
// extend http.IncomingMessage
console.log(req.url) // /api/1?type=123
console.log(req.headers) // header object
console.log(req.method) // GET
next()
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# # Response
Express Response扩展了node http.ServerResponse类,主要是增加一些便捷api以及返回数据时一些默认参数处理。源代码在这 (opens new window) (opens new window)
- 设置响应头
res.getHeader(name, value)``extend httpres.setHeader(name, value)``extend httpres.get(field)底层调用res.getHeader()res.set(field [, value])/res.header()底层调用res.setHeader()res.status(code)底层直接赋值statusCode属性res.type(type)快捷设置Content-Type,底层调用res.set('Content-Type', type)res.cookie(name, value, options)设置指定name的cookie。该功能express提供,而不是cookie-parser包实现。res.clearCookie(name, options)清楚指定name的cookie。
- 发送数据
res.write(chunk[, encoding][, callback])``extend http写入数据res.end([data] [, encoding])``extend http。res.send([body])body可选:Buffer、object、string、Array。除非之前set过Content-Type,否则该方法会根据参数类型自动设置Content-Type,底层写入数据使用res.end()res.json()返回json对象。底层调用res.send()res.redirect([status,] path)302转发urlres.render(view [, locals] [, callback])输出对应html数据res.sendStatus(statusCode)status和send的快捷键
res.type('json'); // => 'application/json'
res.header('Content-Type', 'text/plain');
res.status(404).end();
res.status(404).send('Sorry, we cannot find that!');
res.status(500).json({ error: 'message' });
res.sendStatus(200); // equivalent to res.status(200).send('OK')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# # 路由机制源码解析
路由机制是express精髓。源码中,request、response、view模块都清晰易懂,可能就是router这块容易让人看糊涂。这里对express路由机制源码做下个人整理:
# # express与子路由有相同API
细心的读者可以发现,express实例和new Router()有一样的API:
express/router.use(path, callback)express/router.all/METHOD(path, callback)。all只是METHOD的合集,故分为一类express/router.route(path)
这是因为express实例中保存着一个单例模式的主Router对象(下文都叫主路由),这就意味着Router有的API都可以在express实例上。源码在application.js的137行 (opens new window) (opens new window):
app.lazyrouter = function lazyrouter() {
if (!this._router) {
this._router = new Router({ // 单例模式的Router
caseSensitive: this.enabled('case sensitive routing'),
strict: this.enabled('strict routing')
});
// 默认应用两个中间件
this._router.use(query(this.get('query parser fn')));
this._router.use(middleware.init(this));
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# # express/router.use(path, callback)
use方法一般用于执行中间件。这里为了方便理解,把一些参数处理等干扰代码省略了。我们可以很明显的看到,express.use使用了主路由use方法。所以简单理解express.use(args) = router.use(args)
// application.js L187行
app.use = function use(fn) {
// 获取单例主路由
this.lazyrouter();
var router = this._router;
fns.forEach(function (fn) {
if (!fn || !fn.handle || !fn.set) {
// 交给router对象去处理
return router.use(path, fn);
}
}, this);
return this;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
现在去看下router中use方法,同样去除一些参数处理等干扰代码。最终定义了Layer对象把路径和回调函数做了包装,并把layer压入stack中,方便调用时循环stack以执行匹配的回调函数。
// router/index.js L428行
proto.use = function use(fn) {
// layer对象包装path和回调函数
var layer = new Layer(path, {
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: false,
end: false
}, fn);
// use通常是非路由中间件,故没有route实例
layer.route = undefined;
// 压入stack中,路由匹配时会从stack遍历
this.stack.push(layer);
return this;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# # express/router.route(path)
该方法返回一个Route对象,注意是Route对象,不是Router对象。代码很简单,还是拿到主路由并调用主路由的route方法。
// application L254行
app.route = function route(path) {
this.lazyrouter();
return this._router.route(path);
};
2
3
4
5
6
router.route方法是每次新建一个Route对象(存储了定义的路由METHOD方法),同样经过Layer包装,压入stack,并最终返回该Route实例。所以简单理解,express.route(path) = new Route(path)
重点讲下为什么需要layer.route = route。路由匹配的两个必备匹配条件:path路径 + method方法。express.use这种执行中间件方法只要求有path就可以;express.get/post/...需要同时给到path和method,express.get/post/...底层都会调用express.route以得到一个Route实例。Route实例存储了对应路由上哪些方法被注册,比如只有get方式可以匹配到。所以当实际匹配路由时,从router的stack遍历找到对应layer后,如果是中间件就不找了,如果是路由方法则需要通过layer找到对应Route实例,再继续匹配。
// router/index.js L491行
proto.route = function route(path) {
// 创建了path下的Route
var route = new Route(path);
// 同样用layer包装。
// 注意回调函数传递的是route.dispatch函数,这里是逻辑递增的关键
// 保证了定义在路由上的多个中间件函数被按照定义的顺序依次执行
var layer = new Layer(path, {
sensitive: this.caseSensitive,
strict: this.strict,
end: true
}, route.dispatch.bind(route));
// route方法通常用于路由,需要知道具体的请求method
// 所以需要从statck找到layer,再找到具体route
// route实例上存储了对应path路由的哪些method
layer.route = route;
this.stack.push(layer);
// 返回该route实例
return route;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# # express/router.all/METHOD(path, callback)
该方法用于注册一个get/post/...路由。从源码中可以看出,先实例化一个Route对象,最终执行的是该对象的METHOD方法。简单理解,express.get(args) = new Route().get(args)
// application L472行
methods.forEach(function(method){
this.lazyrouter();
// 新实例化Route对象,并返回
var route = this._router.route(path);
// 执行Route对象的get/post/...方法
route[method].apply(route, slice.call(arguments, 1));
return this;
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
接下来让我们看下Route对象下的METHOD方法。该方法也对回调函数进行了包装并且也存入stack中。由此可知,凡是路由机制API中有回调函数的,都会经过Layer进行包装。路由匹配到的时候会被调用。
// router/route.js L92
methods.forEach(function(method){
Route.prototype[method] = function(){
var handles = flatten(slice.call(arguments));
for (var i = 0; i < handles.length; i++) {
var handle = handles[i];
// 在Route对象中,调用get/post方法也用Layer包装,并存储在stack中
var layer = Layer('/', {}, handle);
layer.method = method;
this.methods[method] = true;
this.stack.push(layer); // 这里是Route对象的stack
}
return this;
};
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# # 路由匹配调用
在哪里判断是否匹配呢?从源码看你能得到app.handle-->Router.handle。以下是抽取的主要代码以及详细注视,以下的代码解释中能理解上面提到的所有内容。随手画了个执行流程图: 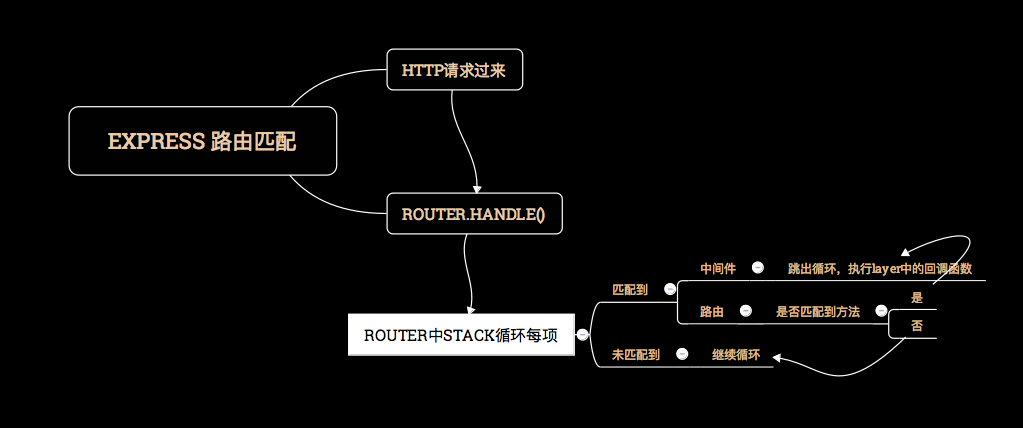
proto.handle = function handle(req, res, out) {
var self = this;
// 拿到主路由的stack
var stack = self.stack;
// next方法循环处理stack
next();
function next(err) {
var layer;
var match;
var route;
// match为true以及idx小于stack长度才继续循环
// 其他情况都跳出循环
while (match !== true && idx < stack.length) {
layer = stack[idx++];
// 匹配path
match = matchLayer(layer, path);
route = layer.route;
// 没有匹配到,继续下次循环
if (match !== true) {
continue;
}
// 无路由的中间件,跳出while循环(此时match = true)
if (!route) {
continue;
}
// 有路由的需要拿到route实例,再判断是否匹配到method
var method = req.method;
var has_method = route._handles_method(method);
// 没有匹配到则继续循环,否则跳出循环
if (!has_method && method !== 'HEAD') {
match = false;
continue;
}
}
// 匹配到的layer都会执行到这
// process_params主要处理express.param API,这里不展开
self.process_params(layer, paramcalled, req, res, function (err) {
if (err) {
return next(layerError || err);
}
// layer的handle_request函数是执行回调函数
// 把next函数传递下去是为了继续循环执行
layer.handle_request(req, res, next);
});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
Layer.prototype.handle_request = function handle(req, res, next) {
var fn = this.handle;
if (fn.length > 3) {
// not a standard request handler
return next();
}
try {
// 暴露给外面的回调函数,包含三个参数req、res、next
// 所以这就解释了为什么一定要执行next()方法才能路由链路一直走下去
fn(req, res, next);
} catch (err) {
next(err);
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# # 总结
- Route模块对应的是route.js,主要是来处理路由信息的,每条路由都会生成一个Route实例。
- Router模块下可以定义多个路由,也就是说,一个Router模块会包含多个Route模块。
- exress实例化了一个new Router(),实际上注册和执行路由都是通过调用Router实例的方法。类似于中介者模式
- 凡事有回调的都是用Layer对象包装,Layer对象中有match函数来检验是否匹配到路由,handle_request函数来执行回调
- 路由流程总结:当客户端发送一个http请求后,会先进入express实例对象对应的router.handle函数中,router.handle函数会通过next()遍历stack中的每一个layer进行match,如果match返回true,则获取layer.route,执行route.dispatch函数,route.dispatch同样是通过next()遍历stack中的每一个layer,然后执行layer.handle_request,也就是调用中间件函数。直到所有的中间件函数被执行完毕,整个路由处理结束。
